Battery
Batteries are always connected and bi-directional, meaning the battery can either be charging, discharging or inactive.
The examples below all assume a battery that is neither empty, nor completely full. In these cases, only one direction of flexibility can be offered.
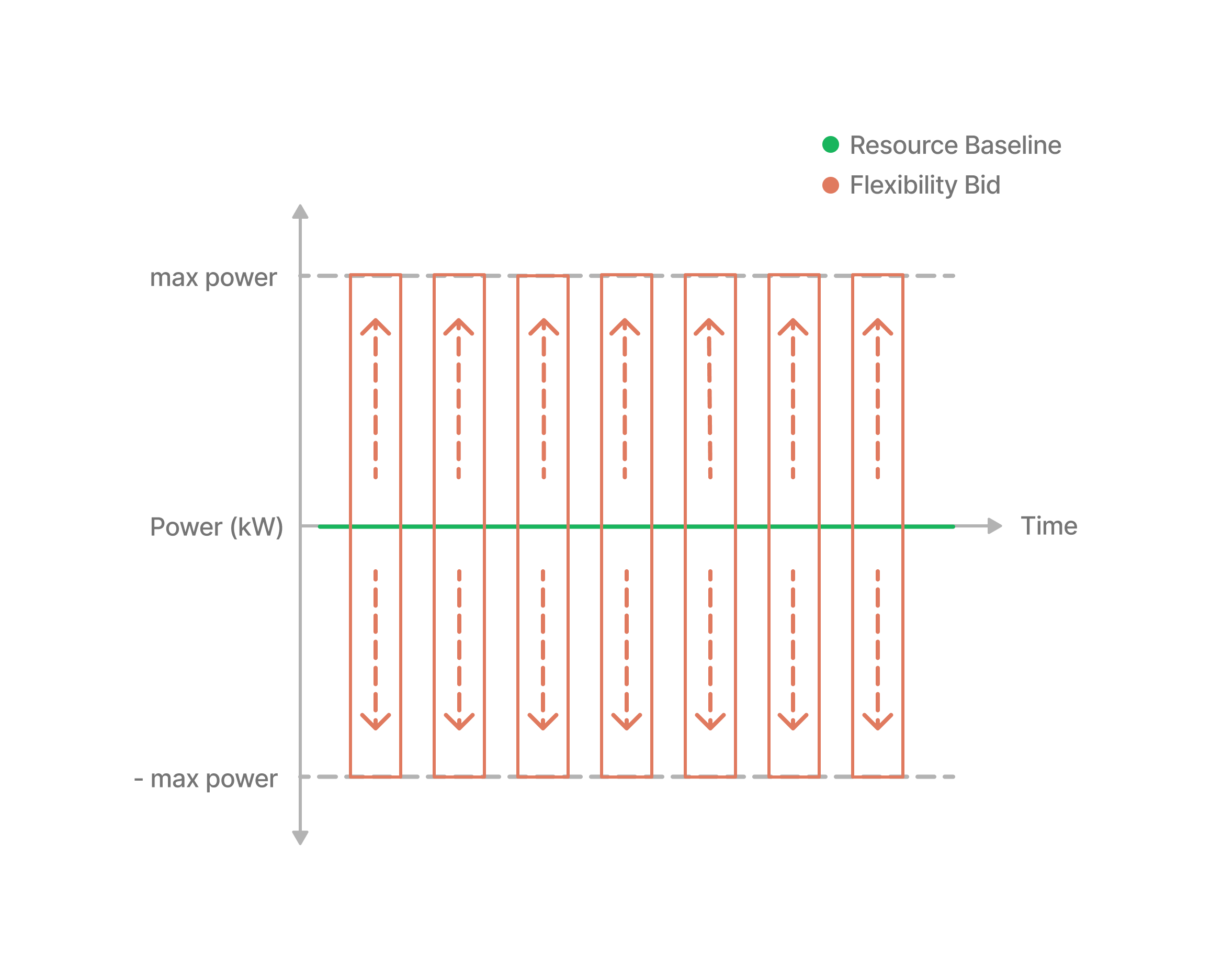
Inactive
Lets start off with the easiest case: the battery is neither charging nor discharging.
This allows us to offer flexibility in both directions.
We can start charging from the grid at max power or start discharging onto the grid at - max power.
Charging
A battery can be charging either from a local PV installation or from the grid. Stopping to consume from the grid, provides flexibility directly. While stopping to consume energy from the PV installation, means that that energy will be injected onto the grid, also providing flexibility in the same direction. Discharging onto the grid also directly provides flexibility in the same direction.
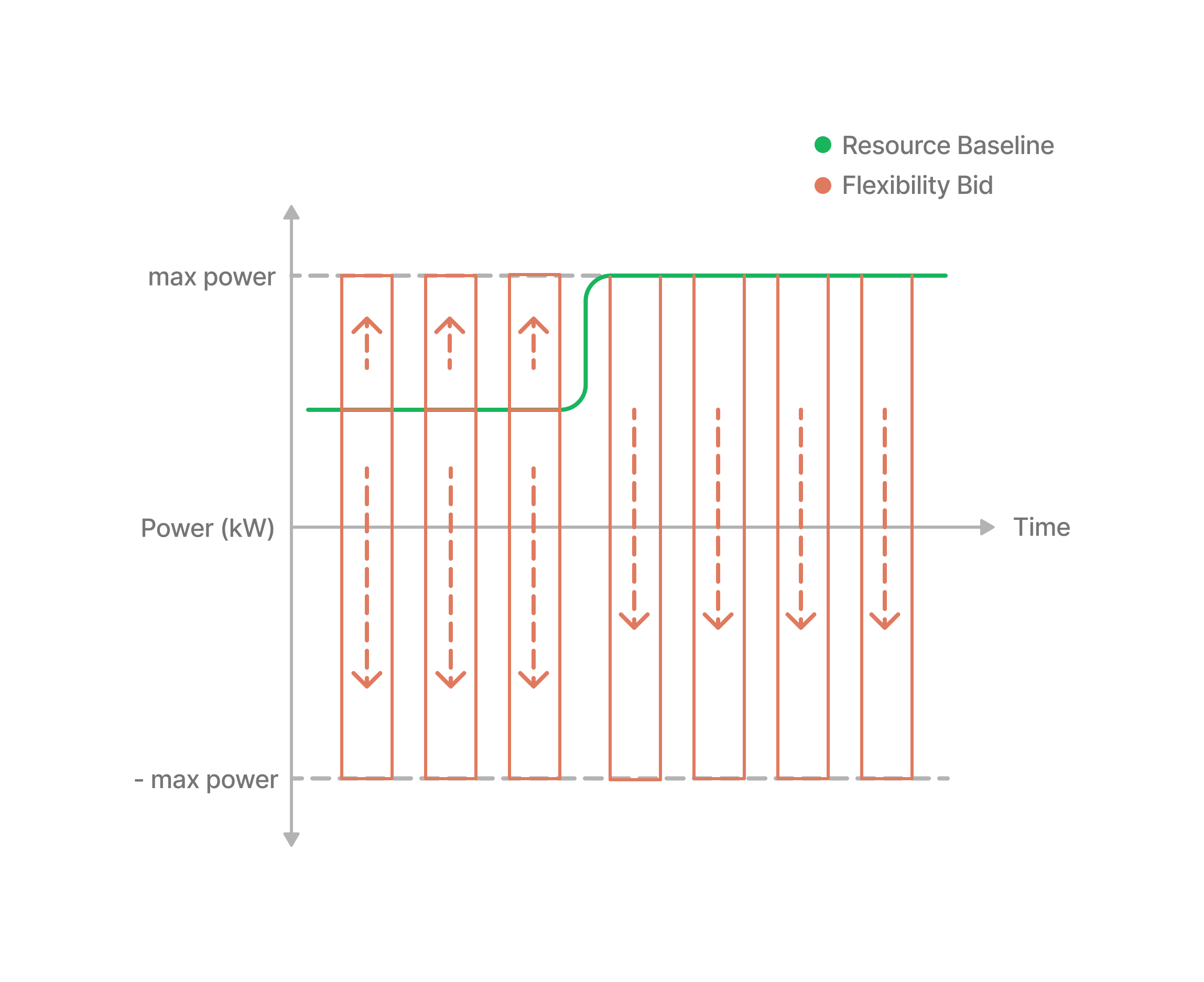
Anytime the battery is charging, we can offer flexibility by stopping to charge and starting to discharge, resulting in flexibility equal to current power + max power.
Going from charging at current power to discharging at max power.
If the battery is below maximum power, we can also offer flexibility in the opposite direction, to charge at max power, resulting in max power - current power of flexibility.
Discharging
A battery is discharging for one of two reasons.
- Serving self-consumption (household appliances, charging an EV, ...)
- Injecting into the grid.
Stopping to discharge provides flexibility in both cases as either (1) the consumption is taken from the grid instead of the battery or (2) we are directly stopping to inject onto the grid. Starting to consume with the battery, also provides flexibility in the same direction.
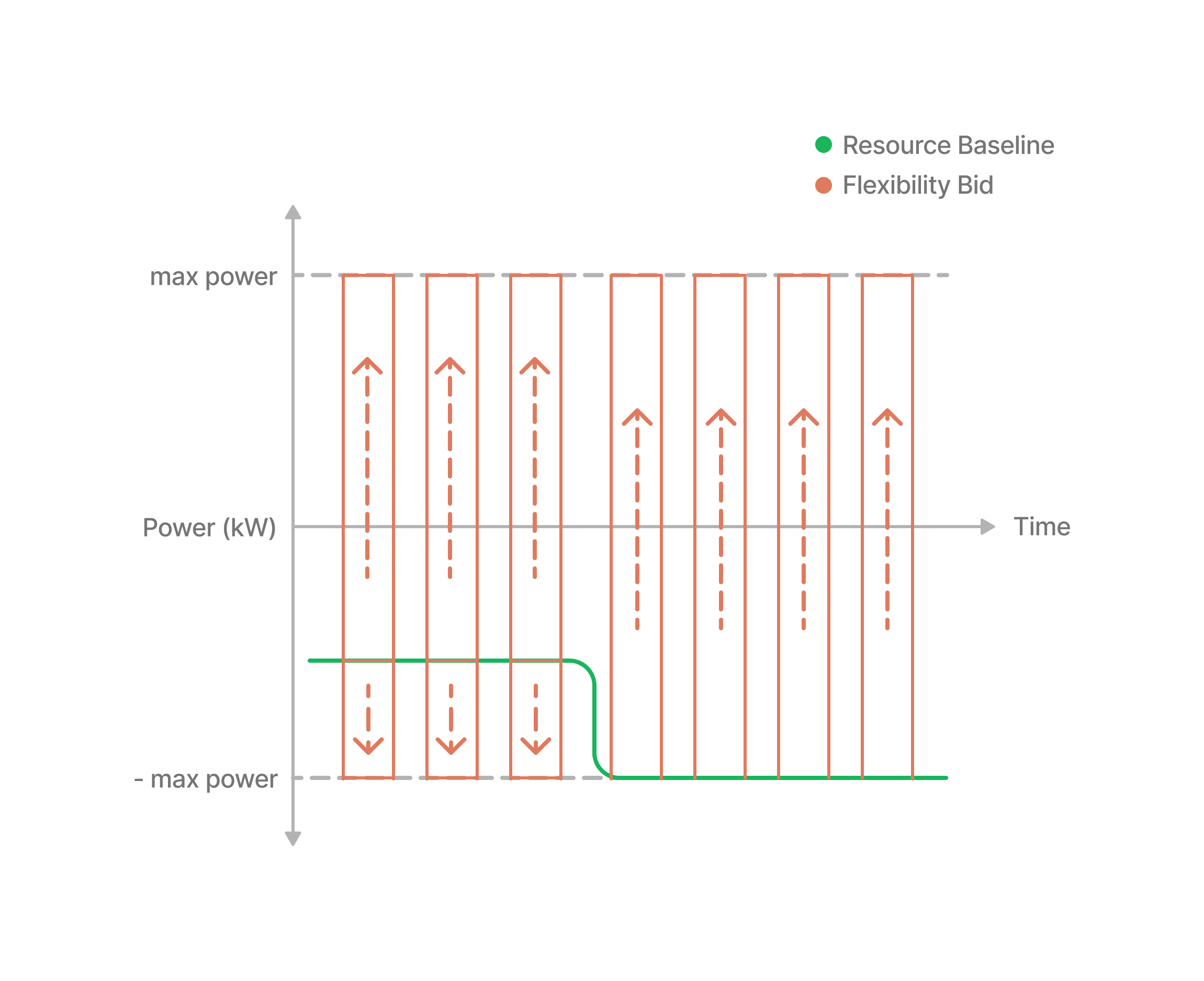
For discharging we are in the same situation as in charging, just the other way around.
So we can provide current power + max power of flexibility in one direction and max power - current power of flexibility in the other.